Case overview
Apart from autonomy, cars have become more connected and smarter through technologies like:
Telematics: Systems that gather and transmit vehicle data for purposes like remote diagnostics, tracking, and infotainment.
Internet of Things (IoT): Connecting cars to the internet enables features like over-the-air software updates, real-time traffic information, and integration with smart home devices.
Safety Features: Connectivity allows for the implementation of advanced safety features such as collision detection systems, automatic emergency braking, and adaptive cruise control.
User Experience: Enhanced user interfaces, voice assistants, and integration with smartphones create a more seamless driving experience.
Business Benefits
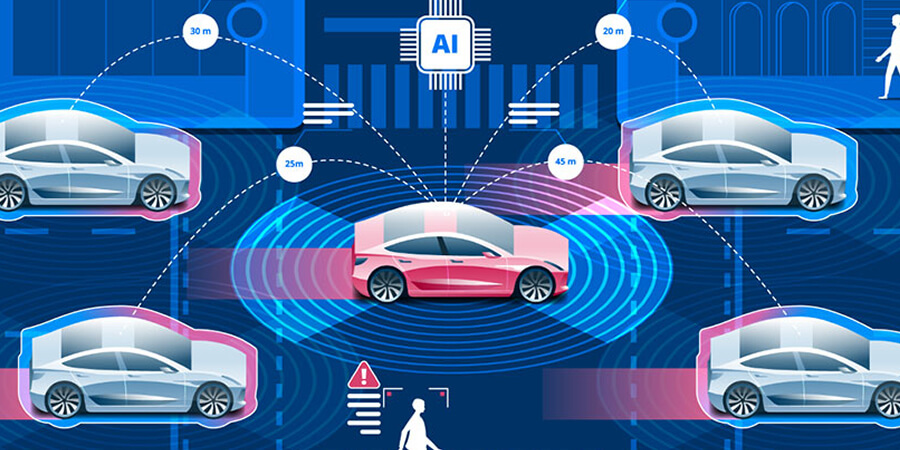

The Brief
The integration of technology into automobiles continues to evolve, promising safer, more efficient, and more convenient transportation. However, it’s a field that requires continuous innovation, collaboration, and careful consideration of ethical and regulatory implications.
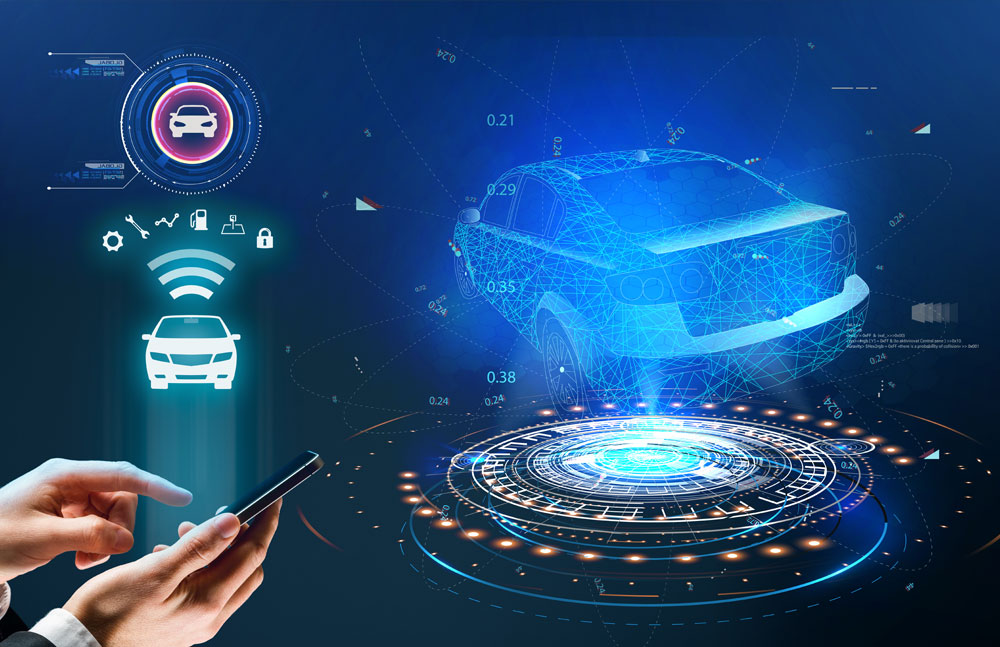
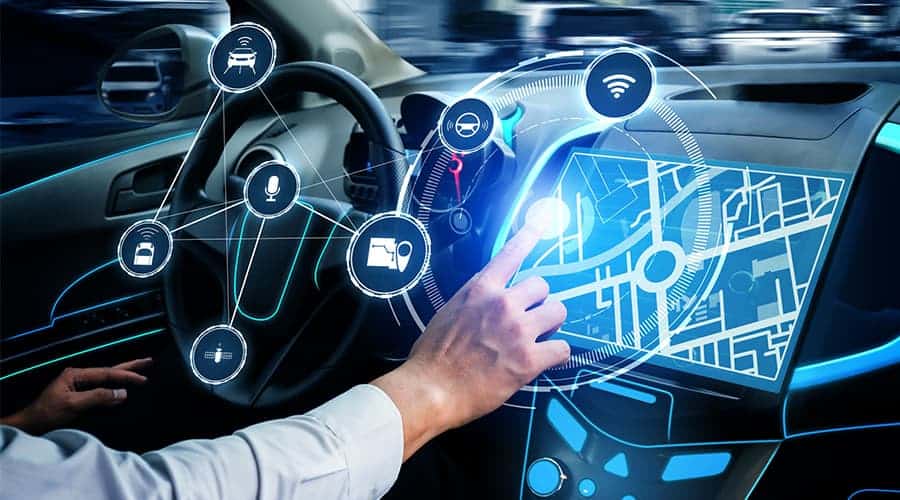



Our Approach
Creating a new approach to connecting cars with technology involves a mix of strategic planning, innovative thinking, and a comprehensive understanding of market needs. Here’s a step-by-step guide to developing a new initiative:
1. Market Research and Needs Assessment:
Identify User Needs: Conduct thorough market research to understand what consumers, businesses, and the automotive industry require. Consider factors like safety, convenience, efficiency, and sustainability.
Competitor Analysis: Study existing solutions, identify gaps or shortcomings, and explore how your approach can offer unique value.
2. Define Objectives and Goals:
Set Clear Objectives: Define what you aim to achieve—whether it’s developing autonomous vehicles, enhancing connectivity, improving safety features, or creating a new user experience.
Establish Metrics: Determine measurable goals to track success, such as adoption rates, user satisfaction, or market share.
3. Technology Integration and Innovation:
Technology Stack: Identify the technologies required—AI, IoT, machine learning, etc.—and plan their integration into vehicles for connectivity, autonomy, and enhanced user experience.
Innovation Focus: Prioritize innovation in areas like user interfaces, data security, AI-driven decision-making, and sustainable energy solutions.
4. Collaborations and Partnerships:
Industry Collaboration: Partner with technology companies, automakers, research institutions, and regulatory bodies to leverage expertise, share resources, and navigate regulatory challenges.
Supplier Relationships: Forge strong relationships with technology suppliers to ensure access to cutting-edge components and solutions.
5. Prototyping and Testing:
Prototype Development: Build initial models or prototypes to test concepts, gather feedback, and iterate on design and functionality.
Real-world Testing: Conduct rigorous testing in controlled environments and on roads to validate safety, performance, and user experience.
6. Regulatory Compliance and Ethical Considerations:
Compliance Framework: Ensure alignment with local and international regulations governing autonomous vehicles, data privacy, and safety standards.
Ethical Framework: Establish protocols for ethical decision-making in scenarios where vehicles need to make split-second choices (e.g., accident avoidance).
7. User-Centric Approach:
User Experience Focus: Design a seamless, intuitive, and user-friendly interface that enhances the driving experience.
Education and Support: Provide resources and educational materials to users for better understanding and utilization of the technology.
8. Continuous Improvement and Adaptation:
Feedback Loop: Create mechanisms for collecting feedback from users and stakeholders to continuously improve the product or service.
Adaptation to Changes: Stay agile and ready to adapt to technological advancements, market shifts, and regulatory updates.
9. Scalability and Sustainability:
Scalable Solutions: Design with scalability in mind to accommodate growth and future technological advancements.
Sustainability Focus: Incorporate sustainable practices and consider the environmental impact of the technology.
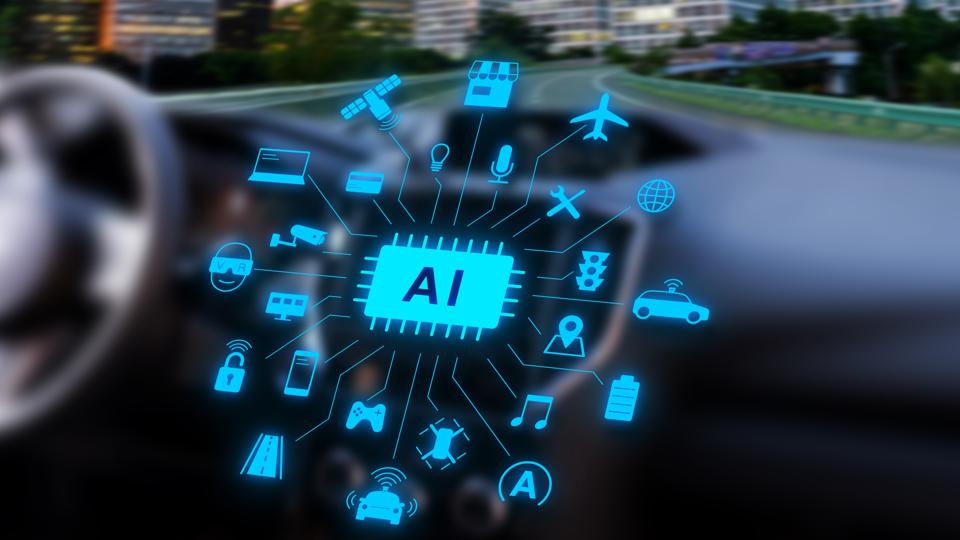
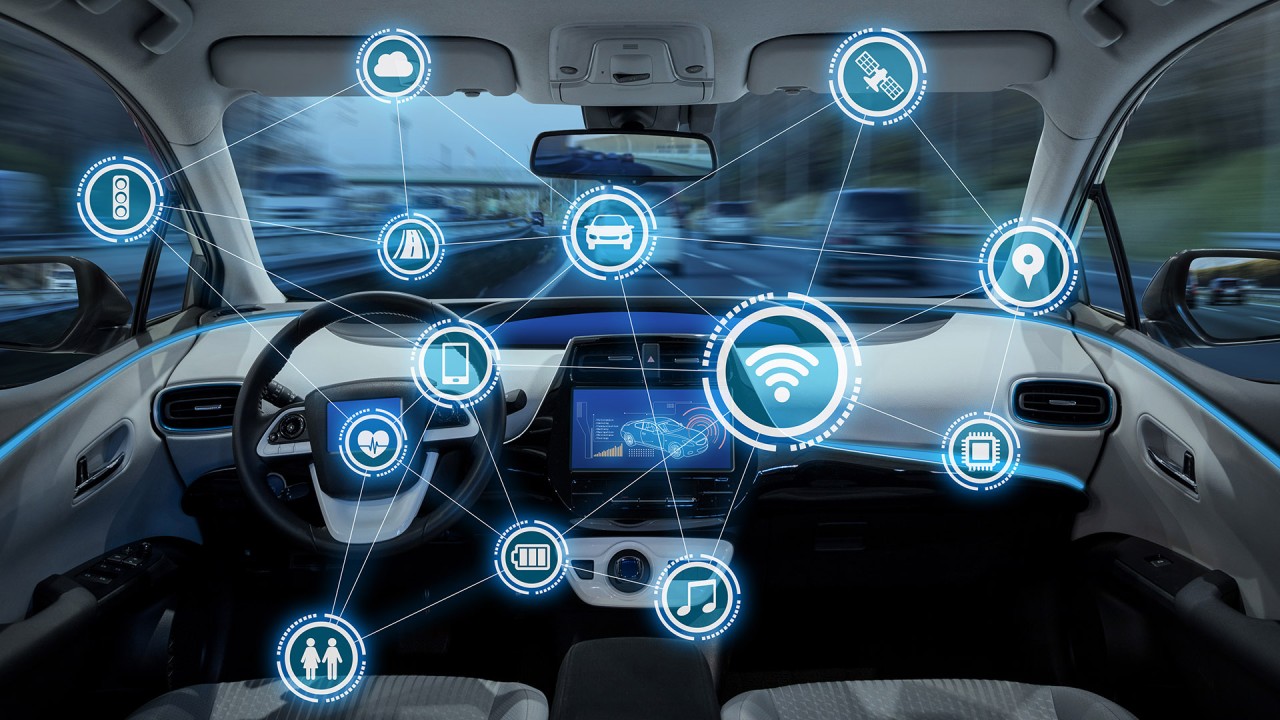


The Results
By following these steps and maintaining a flexible approach that adapts to technological advancements and market demands, you can create a successful initiative that revolutionizes the connection between cars and technology.